Determination of the Heterogeneous Photodegradation Velocity Constant of Sodium Diclofenac with the Evaluation of Residual Toxicity in Artemia salina
Published 2022-12-27
Keywords
- Artemia salina,
- Emerging contaminants,
- Heterogeneous photocatalysis,
- Kinetics,
- Sodium diclofenac
- Toxicity ...More
How to Cite
Abstract
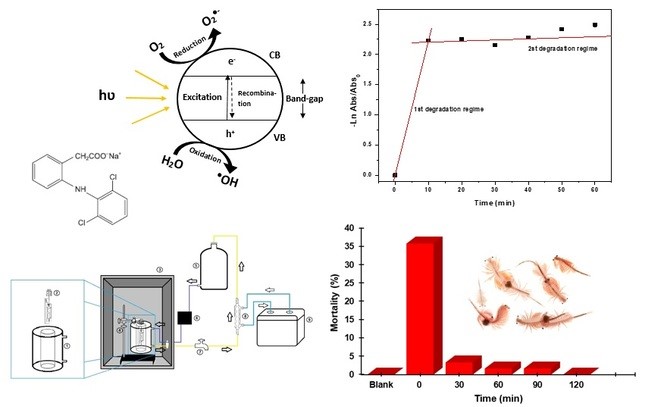
With population growth and increasing urbanization, pollution of aquatic matrices has become frequent, with many studies focused on emerging contaminants as they are recalcitrant and bioaccumulative substances. With the deficiency in conventional water and sewage treatments, this work seeks alternatives for the mitigation of these pollutants, proposing the role of heterogeneous photocatalysis in the degradation of drugs, in this case, sodium diclofenac (SDF). Photocatalytic tests were performed using a bench system. The samples obtained were quantified using a colorimetric method with the aid of a UV-Vis spectrophotometer. The main observation was intense and rapid degradation of the drug in the first 10 min, indicating a reduction in the concentration of 71.05%. For the periods of 0-10 min and 10-60 min, two photodegradation regimes were estimated, with the first regime having an apparent rate constant of 0.12394 min-1 and the second of 0.01601 min-1. Toxicity bioassays were performed with the aid of Artemia salina, determining a 50% lethal concentration of 4.45 x 10-4 molL-1. When performing a new photocatalysis to determine the toxicity of the waste generated it was possible to observe a significant decrease in toxicity in the first 30 min, reaching a total reduction in 120 min.




