Copper Complexes with Polypyridyl Tridentate Ligands and their Biological Significance: A Review
Published 2025-09-05
Keywords
- Bio-applications,
- Coordination geometry,
- Copper-polypyridyl complexes,
- Dipicolylamine,
- Terpyridine
How to Cite
Abstract
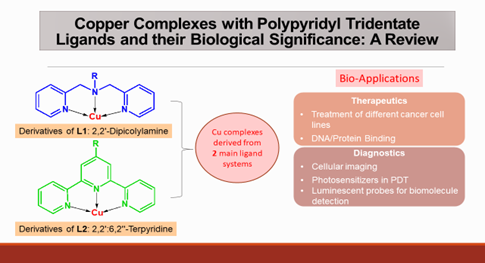
Copper based metal-organic complexes have been evaluated for their suitability as potential therapeutic and diagnostic agents as an attempt to overcome the limitations of the initial platinum-based drugs, including low selectivity, acquired resistance to the introduced drugs and the subsequent side effects. Copper containing complexes, particularly with tridentate NNN coordinating ligands having polypyridyl groups, such as 2,2'-Dipicolylamine and 2,2':6,2"-Terpyridine, are promising alternatives as they entail versatility in their structures and possess chemical and electronic properties which facilitate their targeted cytotoxic and diagnostic activities. Delocalization of excited electrons within the planar, conjugated structures, along with the display of metal to ligand charge transfer transitions (MLCT) leading to intense fluorescent signals, have elevated the suitability of these ligands for the synthesis of biologically beneficial complexes. This itinerary contributes to the popular global trend in the development of more effective chemotherapeutic and theranostic agents.




