Evaluating Norbornadiene/Quadricyclane for Solar Thermal Energy Storage: A Systematic Review Using Methodi Ordinatio
Published 2026-02-19
Keywords
- Methodi Ordinatio,
- Norbornadiene,
- Quadricyclane,
- MOST,
- Review
Copyright (c) 2026 Orbital: The Electronic Journal of Chemistry

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
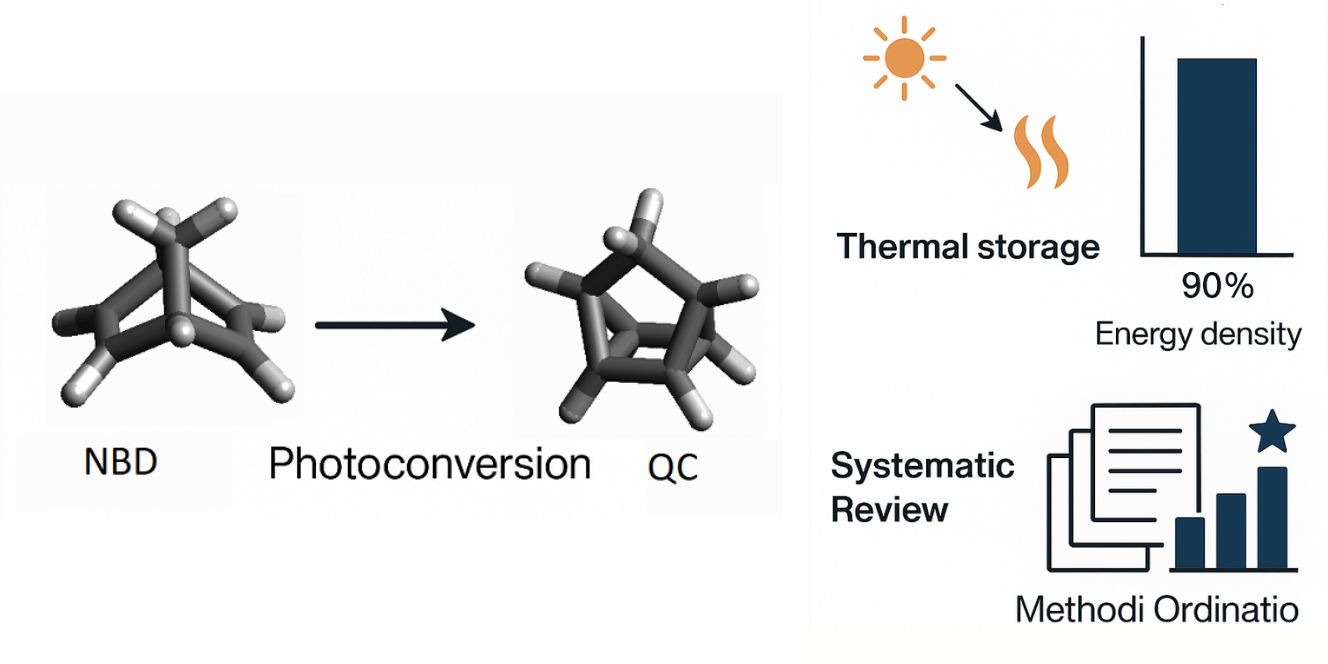
Abstract
This work presents a comprehensive systematic review of the potential of Norbornadiene/Quadricyclane (NBD/QC) as a promising molecular system for solar thermal energy storage (MOST). Utilizing the Methodi Ordinatio methodology, this study aims to identify, classify, and rank the most impactful research articles based on a weighted combination of their citation count, impact factor, and year of publication. A complete literature search was performed across the Scopus, ScienceDirect, and Web of Science databases using targeted keywords such as "Norbornadiene," "Quadricyclane," and "solar thermal energy storage." A complete literature search across Scopus, ScienceDirect, and Web of Science using targeted keywords initially identified 567 studies; after applying relevance criteria, 341 articles published between 2014 and 2024 were selected for detailed analysis. The saved studies were then ranked using the InOrdinatio index, ensuring a data-driven prioritization of the most relevant contributions to the field. The analysis highlights recent technological advancements in NBD/QC-based solar energy systems, focusing on photoconversion efficiencies exceeding 90%, energy densities reaching up to 966 kJ/kg, improvements in isomerization kinetics, and enhanced thermodynamic stability of their metastable states. This systematic review not only contributes to the growing body of knowledge on molecular solar thermal systems but also offers strategic reflections for advancing sustainable and efficient solar energy technologies.




