3D-QSAR, ADMET and Docking Studies for Design New 5,5-Diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione Derivatives Agents Against Cervical Cancer
Published 2022-04-08
Keywords
- 3D-QSAR; 5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4- dione; ADMET; Cancer; Molecular docking
How to Cite
Abstract
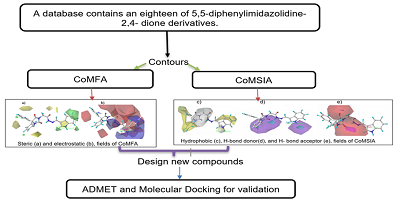
Cancer is one of the world's causes of death, which requires the discovery of new molecules likely to become anticancer drugs. In this study, a three–dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship is employed to study eighteen compounds of 5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione derivatives against cancer cell lines HeLa, their pIC50 varied from 3.62 to 5.00. In addition, the 3D-QSAR model was defined on the basis of Comparative Molecular Field Analysis (CoMFA) and Comparative Molecular Similarity Indices (CoMSIA) analysis, the model achieved strong predictability with the model CoMFA is (Q2 =0.70; R2 =0.94; r2 test =0.96) and the best one on CoMSIA (Q2 =0.73; R2 =0.97; r2 test= 0.98), respectively. We have proposed four compounds with highly potent anticancer predicted activities, based on successful results obtained by the contour maps formed by the method model. Furthermore, the ADMET properties of these newly designed compounds were in silico evaluated, among which two derivatives have respected these properties. These compounds were further evaluated by molecular docking, showing that two molecules T2 and T4 exhibit favorable interactions with the targeted receptor and a high total score. These findings may afford valuable more information to design compounds anticancer activity against Hela cells.
