Remaining Capacity Estimation of Lead-acid Batteries Using Exponential Decay Equations
Published 2021-12-30
Keywords
- Ah counting; Battery management systems; Capacity estimation; Lead-acid batteries; State of charge
How to Cite
Abstract
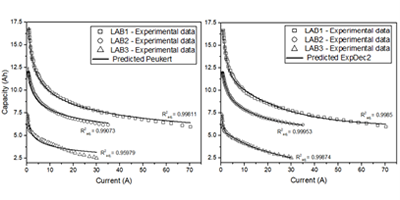
The precise capacity estimation of batteries can extend their lifespan and is necessary to ensure reliability and safety of operation. Many methods have been developed with this objective in the last decades. However, there is still research for more accurate and less complex methods in order to estimate the state of charge of operating batteries. This article presents exponential decay equations that model the behavior of the battery capacity drop with the discharge current. Experimental data for different application batteries showed that these equations have a superior accuracy compared to the empirical Peukert equation. Their parameters are dimensionally coherent and make the characterization and categorization of batteries possible, besides, they give insights about the behavior of the electrodes under different discharge rates. Due to the low complexity and easy adaptability to the currently employed methods, these equations can be easily employed in battery management systems without the need for great computational power.
