Published 2021-03-30
Keywords
- Fuels,
- Higher heating value (HHV),
- Mathematical modeling,
- Proximate analysis
How to Cite
Abstract
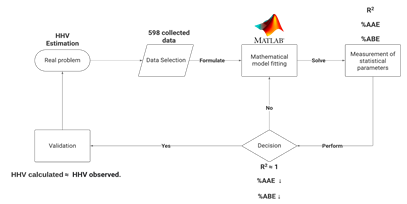
In the world of renewable energies, biomass will play a fundamental role in the coming years, this is how the interest in taking advantage of biomass from lignocellulosic materials is increasing. The objective of the present investigation was to develop a mathematical model for the prediction of the higher heating value (HHV) of lignocellulosic materials. Based on the proximate analysis of the raw materials, 598 data were collected from which possible correlations were established that allowed the development and validation of five statistical models; the best model proposed in the present study considers fixed carbon and ash content as variables, this model presents an average absolute error of 7.03% and an average bias error of 0.91%, in addition to presenting an R2 of 0.801. Being the equation that provides the smallest error in relation to the higher heating value observed.
