Spectral Voltage Contour Plots of Optical Constants and Interface Parameters of the Active Layer of a Multilayer Structure Suspended Particle Device Smart Window from Clear on to Dark off States
Published 2023-04-05
Keywords
- optical constants, multilayer smart windows, suspended particle devices.
How to Cite
Abstract
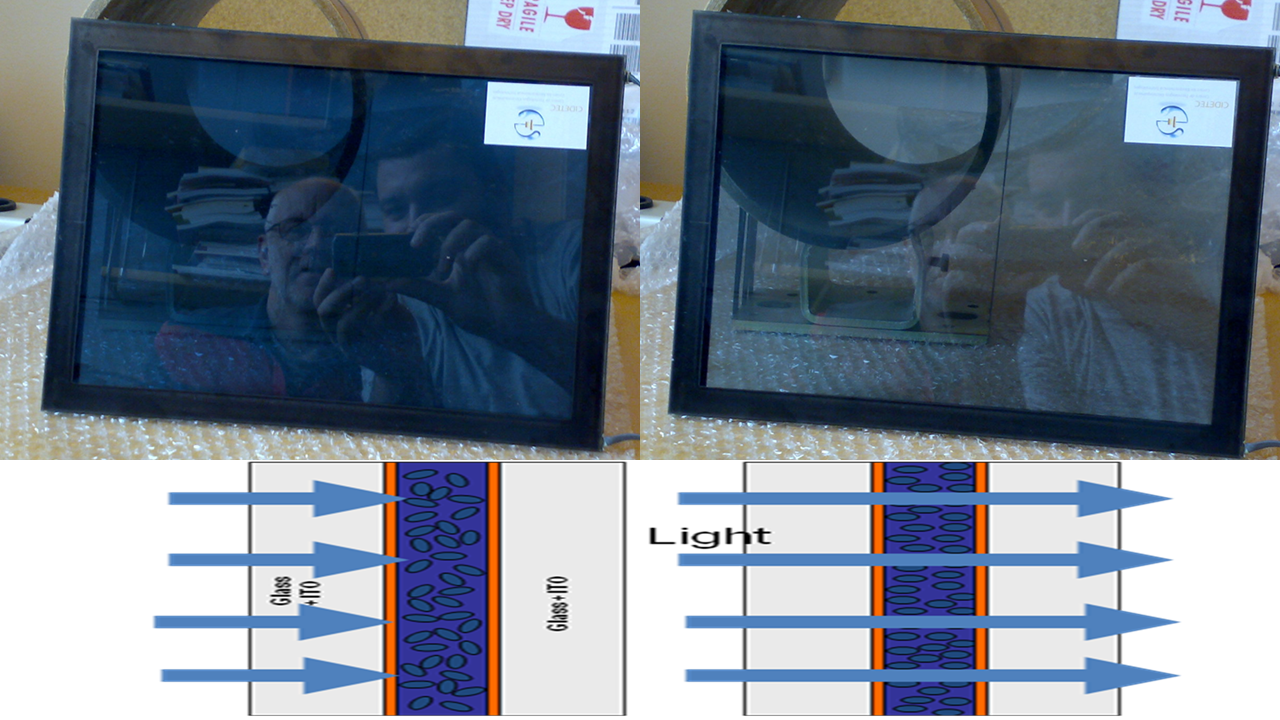
Smart windows based on suspended particle devices (SPDs) are able to switch optically from dark to clear visual appearance when applying an AC electrical signal. This effect is due to light absorbing nanoparticles that get aligned by the applied voltage. The sandwich structure of an SPD consists of several layers and includes two outer glass substrates, each one covered on its inwards-facing side with a transparent conducting thin layer surrounding the centrally positioned SPD active layer. A knowledge of the optical constants of each layer—i.e., the complex refractive index, including its real and imaginary (absorption) parts—is a key in the design of the visual appearance of the SPD window and is a useful tool to determine the optimum thickness of the active layer.




