Advancement of Novel Graphene Oxide Embedded Alumina Nickel Composite Coating Developed at Various Current Densities to Evaluate Corrosion Resistance
Published 2023-04-12
Keywords
- Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, electrodeposition, Nickel GO/ alumina, Potentiodynamic polarization,
How to Cite
Abstract
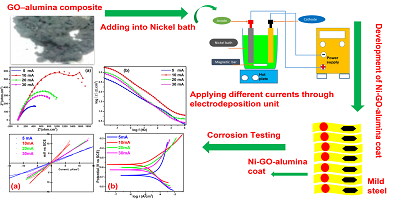
In this research, the influence of deposition current density on the properties of nickel-Graphene oxide/alumina coatings produced by electrodeposition was examined. Nickel matrix composite coatings with graphene oxide doped Alumina (GO-Al2O3) particles were prepared via electrodeposition. When embedding GO-Al2O3 particles in the Ni matrix, remarkable anti-corrosion properties are anticipated due to the outstanding mechanical properties of GO and Al2O3. The structure, content, and morphology of GO, GO-Al2O3, and coatings deposited at various current densities were determined using X-ray diffraction, Fourier transforms infrared spectroscopy, Field emission Scanning electron microscopy, and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. GO-doped alumina particles were successfully incorporated into the matrix of nickel, according to the findings. Porosity measurement and cross-sectional thickness were also investigated at various current densities. Potentiodynamic polarization testing and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy were used to study the coatings' corrosion-resistant characteristics. According to the findings, coatings developed at high current densities, such as 30 mA cm-2, are porous and not uniform in nature. Furthermore, at high current densities, the content of GO and Alumina is reduced, resulting in a decrease in mechanical and corrosion resistance. Due to its less porous and uniformly formed coating, 10 mA cm-2 was the optimum current density for achieving the most desirable features.




