Evaluation of the Efficiency of the Reuse of Sorbents and their Modified Forms for the Removal of Copper Ions from Water
Published 2025-05-03
Keywords
- Spent sorbent,
- Regeneration,
- Modification,
- Copper (II) ions,
- Removal
- Adsorption ...More
How to Cite
Abstract
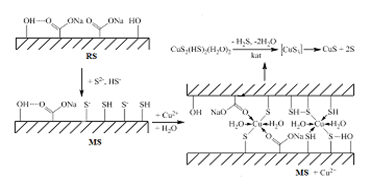
In recent years, spent kieselguhr and activated carbon are considered not as waste, but as secondary raw materials. The purpose of the work is to investigate the effectiveness of using a previously regenerated spent food industry sorbent modified with sulphide and hydrosulphide ions for adsorption removal of copper (II) ions from water. A comparative analysis of the degree of removal and adsorption of copper (II) ions by the regenerated sorbent (RS) and its modified form (MS) was carried out. Insignificant adsorption of Cu2+ on the surface of the regenerated sorbent (RS) is explained both by the nature of the adsorbate and the morphology of the adsorbent after its acid-alkaline activation. Sorption of Сu2+ ions is mainly carried out by carboxyl groups. Modification of the regenerated sorbent surface with more active sulphide and hydrosulphide ions leads to a significant increase in its selective adsorption in relation to copper (II) ions. It was established that topochemical reactions of formation of copper (II) sulphide CuS and elemental sulphur take place on the surface of the modified sorbent (MS). The possibility of topochemical transformations has been established by IR-spectral and XRD studies. The use of a sorbent modified with sulphide and hydrosulphide ions increases the removal of copper (II) cations from the studied solutions by 65.5 times. The obtained results allow us to recommend the use of a regenerated sorbent (RS) of the food industry, modified with sulphide and hydrosulphide ions, to remove copper (II) ions from water.




