Strontium Titanate (SrTiO3) for Adsorption of Cd(II) Ions and Photodegradation of Methylene Blue Dye in Aqueous Solutions
Published 2025-05-30
Keywords
- Adsorption,
- Hydrothermal-microwave,
- Photocatalysis,
- Polymeric precursors,
- SrTiO3
How to Cite
Abstract
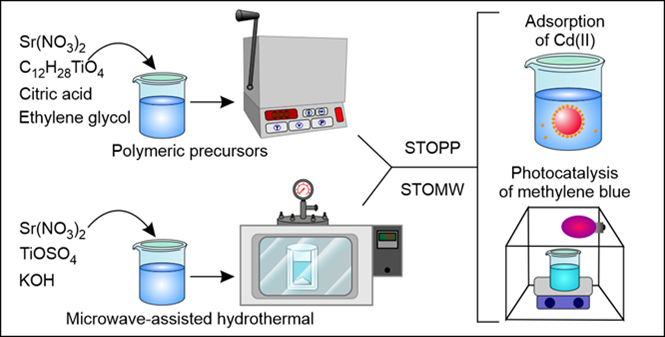
Strontium titanate (SrTiO3 – STO) is a metal oxide with a perovskite structure that has attracted scientific interest due to its various applications. The present study aims to synthesize STO and evaluate its potential for adsorption of Cd(II) ions and photodegradation of methylene blue. The STO samples were synthesized using the polymer precursor method and microwave-assisted hydrothermal method. X-ray diffraction analysis confirmed the formation of STO crystalline phase, and scanning electron microscopy revealed differences morphology to distinct synthesis method used. STOMW sample was able to remove 94.7% of Cd(II) ions in solution, while STOPP sample demonstrated good photocatalytic activity, with 80% dye degradation. The results indicate that STO is a promising material for the removal of both inorganic and organic contaminants from aqueous waste.




