Published 2021-06-30
Keywords
- Acid medium,
- Aqueous extract,
- Electrochemical,
- Green inhibitors
How to Cite
Abstract
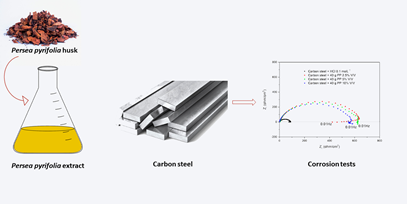
Carbon steel is one of the most widely used alloys in industrial applications. However, the use of this metal may be limited because of corrosion tendency. Thus, it is necessary to develop methods that inhibit its degradation. One way to inhibit corrosion is to use organic inhibitors. Some organic compounds with heteroatoms inhibit corrosion by forming a protective film. In this study, the corrosion inhibition of carbon steel 1020 in 0.1 mol L-1 hydrochloric acid medium was evaluated. The natural inhibitor used was an aqueous extract of the bark of Persea pyrifolia (PP) plant at concentrations of 2.5, 5 and 10% V / V. The electrochemical response was determined by open circuit potential measurements, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, and anodic potentiodynamic polarization. Therefore, mass loss was measured, and inhibitory efficiency was evaluated. The best results were observed for the concentration of 2.5% V / V of Persea pyrifolia extract, presenting and inhibition efficiency of 82.5% on the 1020 carbon steel. The electrochemical results indicates that PP extract can be used as green corrosion inhibitor in acidic medium.
