Published 2025-07-05
Keywords
- Antibacterial,
- Antibiotic,
- Hydrazone,
- Lichen,
- Structure modification
How to Cite
Abstract
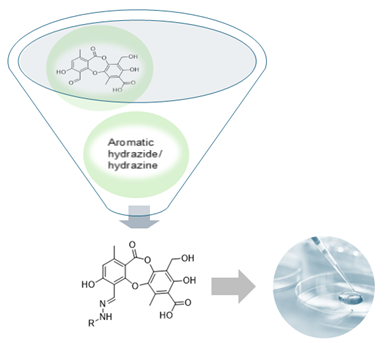
Antimicrobial resistance has become a serious threat worldwide. To overcome this huge public health problem, the continuous search for new active compounds is urgently needed, and structural modifications and the synthesis of natural products derivatives are valid strategies to find active substances and enrich the understanding of correlations between structure and biological activity. Hydrazones and acylhydrazones were synthesized from protocetraric acid, a lichen depsidone, and evaluated for antibacterial activity against S. aureus and E. faecalis. Some hydrazones showed enhanced activity compared to the natural product, especially p-chloro and p-bromophenyl hydrazones, with MIC values ranging from 15.6 to 31.25 µg/mL.




